Latest Posts
Which is better for long-term data storage: solid state, mechanical, mobile (OTG USB), or SD card?
Let’s start with a look at the different data storage options.
Mechanical hard disks use magnetic discs as storage media:
The shelf life of HDD data retention kept properly is 100 years (calculated by some foreign institutions. God knows how).
Other considerations, however, must be addressed.
1.Now all mobile hard disks are 2.5-inch, and almost all 2.5-inch disks are SMR (shingled). In summary, when you make a cold backup of some data, you risk causing the preceding data to be read and written improperly when you operate other data later (for more information, see the SMR and PMR sections below).
2.Vibration, impact, and falling are the three things that mechanical hard drives are most scared of. There is also disturbance and degaussing of strong magnets.
To summarize, a mechanical hard drive has a lifespan of 4-7 years, but even if it is accidentally broken or deleted, the contents on the disk may still be recovered using special technology. So, its file preservation security is far superior to that of solid state.
What type of hard drive is utilized for long-term data storage?
A 3.5-inch mechanical hard drive, preferably a PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording) hard drive.
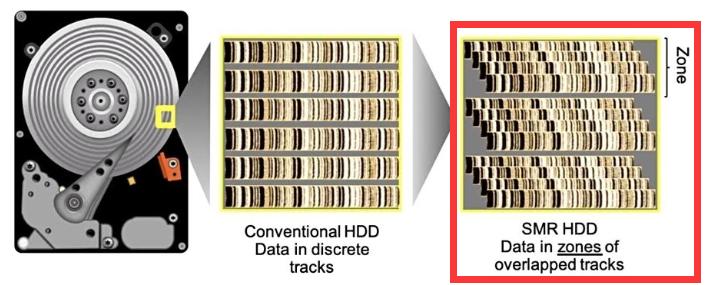
The distinction between a vertical and a shingled disk
The vertical technology PMR is shown on the left, with the track gap clearly visible. The shingled technology SMR is shown on the right, with the tracks overlapping.
A mechanical hard disk with “perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) technology” is referred to as a vertical hard disk.
Toshiba introduced it in 2004. Its benefits include quick random read and write, as well as a long lifespan.
The shingled hard disk is a novel technology that was designed to increase the hard disk’s capacity.
A mechanical hard drive’s capacity can be increased in just two ways:
One method is to expand the storage capacity of a single disc.
The maximum capacity of a single vertical hard disk is around 1.6TB.
The other option is to increase the disc count. Two-disc sets are more common, but three-disc sets are also available.
In reality, the shape of a hard drive, such as the Seagate hard drive in the image below, can reveal this.
Although there are fewer discs in the deeper recesses of the red frame, this is unimportant. In any case, if you plug it in hard, you’ll get three disks. But please do not worry about the number of disks.
There is “shingled magnetic recording technique” to continue to enhance capacity.
A shingled hard disk’s tracks are layered one by one like tiles, and its primary function is data writing. The speed will be slow, especially when the data on the hard disk is often wiped or written, or when fragmented files are written. Sudden speed decreases are also possible, and severe sudden speed drops will cause the system to crash or the game to halt. Furthermore, shingled hard drives alter the distribution of tracks. Because the operation of shingled erasing + overwriting data requires the head to write data twice (you need to open the upper tile to write to the stacked tile), you must erase first and then write. This will undoubtedly increase the load on the hard disk, make it more noisy while working, and shorten its life.
Manufacturers often include a huge cache in order to improve read and write performance. It is usually 128MB or 256MB. The data of the top tile is vacated into the cache, and then the data of the upper tile is written back after the data of the lower tile is written.
As a result, you should be cautious if you notice promotional wording like “ultra huge cache.” Basically, disks larger than 128MB cache are Shingled tray.
If you have heard of NAS, you have undoubtedly heard of Synology as well. Despite the fact that this type of hard drive is claimed to be “built specifically for NAS,” Synology has declared on its official website that all versions do not support Western Digital Red Drives (2TB to 6TB capacity models) that use SMR technology.
“Due to performance characteristics of SMR drives, this model is only suitable for light workload environments,” Synology notes.
QNAP that specializes in network-attached storage appliances has similar suggestions.
Western Digital red drives that use SMR shingling technology are still listed on the hard drive compatibility list, but there is a disclaimer that says: “NAS performance may be impacted when utilizing SMR-based hard drives if the disk runs out of cache.We propose data center hard drives if your NAS is used in a data-intensive setting.”
To prevent generating problems for consumers, these professional server providers advise keeping away from shingled disks. As a result, for disks that are regularly read and written, we should avoid these pits as much as feasible.
For mechanical hard disks, we recommend enterprise disks, such as the Seagate Galaxy, Western Digital’s UltraStar, and Toshiba’s MG07 series. Any 2.5-inch mechanical disk, mixed disk, is not taken into account.
Toshiba P300 Mechanical hard driveSeagate Enterprise Hard Disk【ST2000NM000A】Western Digital (WD) Desktop Hard Drive (WD40EZAZ)Solid-state drives use flash memory chips as storage media:
One-time write, the shelf life of reasonable static placement is also 100 years (emmm).
1.The control of the gate voltage, which represents 0 and 1, is the storing concept of flash memory chips. The amount of electrons in the gate has a positive relationship with the voltage. Long-term deployment will test the insulating layer’s and floating gate’s ability to retain electrons. It will shift from 1 to 0 when the leakage reaches a specified amount.
2.The 01 secondary scenario described previously is still SLC, and just the secondary voltage must be controlled: Vth is 1 when it is above a particular threshold and 0 when it is below, implying low control precision. MLC is a four-level control: every 25% corresponds to 00 01 10 11, which has a better precision control. TLC is divided into eight levels, with each 12.5% corresponding to 000 001 010… QLC is the sixteen-level control: every 6.25% corresponds to 0000 0001…. In other words, the higher the number of voltage control levels, the less stable the data retention.
3.The erase and write life of the flash memory chips is limited. SLC chips (100,000 erase/write cycles) are the most powerful. TLC chips (1-3000 erase//write cycles) are presently the most common. MLC (3-10000 erase/write cycles) is not widely available, but QLC (500-1000 erase/write cycles) is ready to use.
When converted to current household read and write volume, SLC can be used as a family heirloom (hundreds of years of life), MLC can be used up in this life (less than 100 years), TLC and the host have the same lifespan (approximately ten years), and QLC is expected to be three to five years.
However, you must take into account the growing amount of data. Ten years ago, an 80GB hard disk was sufficient, and a month’s worth of data was only one or two gigabytes. Mechanical hard disks with a capacity of 500 GB and solid-state hard disks with a capacity of 240 GB are now frequently utilized. An average person’s daily upload or download of files and emoticons on platforms like Facebook, Ins, and WhatsApp amounts to one to two gigabytes. What will it be like in ten years?
To summarize, a solid state drive has an average lifespan of 5-8 years. But once it is destroyed, data retrieval is far more difficult than with a mechanical hard disk.
In this case, too, enterprise solid state drives are recommended:
The first is the P4800X series of Intel Optane chips, which are the top of the line (we have little information about Optane chips, but 30 full-disk reads and writes a day are enough to show its power).
SLC chips: Samsung 983ZET (Intel also has SLC, but I did not find it);
MLC particles ( eMLC or HET-MLC are better):
M.2 NVME protocol: Samsung SM961=Samsung 960PRO>Toshiba XG3
M.2 NGFF protocol: Intel S3520 > Intel S3500
(The M.2 interface solid state drive is not recommended since it has a lower read and write life than the other three types of SSDs with different interfaces.)
SATA interface: Intel S3710=Samsung SM865a>Intel S3610=Samsung SM863a
U.2 interface: Intel P3700 series, Intel 750
Bulk Usb flash are substantially flash memory chips:
High-end bespoke U disks are recommended:
Mostly commonly used: Yincan IS903 master+HET-MLC/eMLC;
High-end: Huirong SM2246EN master + ASMedia1153E bridge + SLC chips;
The U disk is not suggested for long-term data storage. It is merely a delivery truck.
I am not familiar with SD card internals. Its stability, on the other hand, is truly indescribable… It is strongly advised against using SD cards for long-term storage.
Finally, it is suggested that SSD be used for daily data storage and that HDD be used to make a cold backup of a mechanical hard disk once a year. Store the HDD in a moisture-proof cabinet. One person’s data storage costs for a year are 500 RMB (half of an 8T mechanical disk) + 300 RMB (moisture-proof cabinet) + 100 RMB (electricity bill).













Leave a comment